With greater computing potential comes an unprecedented hunger for data. From 2010 to 2020, the quantity of data worldwide rose by over 5,000%, with usage forecasted to continue increasing rapidly in the coming decade.
Data centers didn't meet this staggering demand increase with only physical expansion but also with increasingly advanced technology, such as edge computing and bare metal cloud.
7 Data Center Technology Trends for 2023
IT experts do not expect a revolution in data center technology in the coming year, rather an evolution of current technologies and practices.
Here are 7 of the most impactful technology trends shaping the data center industry.
1. Cloud Computing Isn’t Going Anywhere
Cloud computing enables using resources such as servers, storage, and applications, over the internet, without investing in and managing physical hardware and infrastructure.
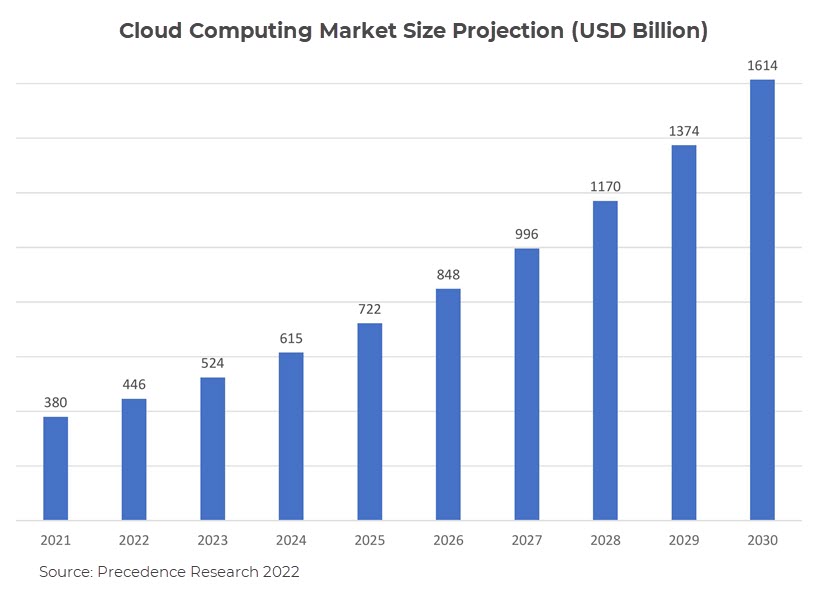
The continued rise of cloud computing is the single most dominant trend shaping the data center industry. Despite inflation and worsening macroeconomic conditions, Gartner predicts worldwide spending on public cloud services will grow 20% in 2023.
However, according to Flexera's 2022 state of the cloud report, organizations are putting more effort into managing usage and cutting costs to control growing cloud bills. Optimizing the current use of the cloud was listed as the top initiative reported among organizations, followed by migrating more workloads to the cloud.
Adapting to market changes quickly and easily can help avoid over or under provisioning resources. phoenixNAP's flagship product Bare Metal Cloud enables customers to instantly scale their use of cloud resources via API or CLI.
2. The Further Development of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud technology combines the benefits of both public and private clouds while mitigating the weaknesses of each.
For example, an organization can store sensitive data on a private cloud while leveraging a public cloud's cost savings and flexibility for less critical workloads. Additionally, a hybrid cloud allows organizations to move workloads between private and public clouds as needed or take advantage of the expertise and resources of multiple cloud providers – a great benefit for organizations with complex or specialized needs. Furthermore, it prevents vendor lock in, thus providing more fluid infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud is now more popular than ever. According to Cisco's 2022 Global Hybrid Cloud Trends Report, 82% of surveyed IT leaders say they have adopted hybrid cloud to some extent. Additionally, 47% report deploying between two to three public infrastructure as a service clouds, while only 8% of organizations report using only a single public IaaS cloud provider.
To learn the differences between public and private cloud, read our article Public vs. Private Cloud: Differences You Should Know.
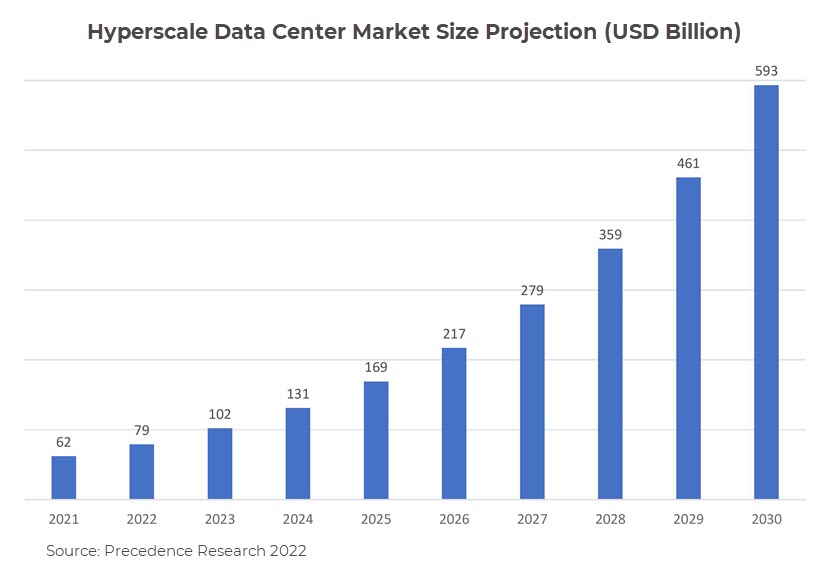
3. The Dominance of Hyperscale Data Centers
Hyperscalers are large-scale data centers designed to support the rapid and seamless deployment of a large number of servers. They are typically much larger and more complex than traditional data centers, supporting the needs of internet giants and other companies that generate and process vast amounts of data.
Another key difference from regular data centers is the level of automation needed because of the sheer size and complexity of the workloads. Hyperscale data centers often use modular designs and prefabricated components, allowing quick construction and easy expansion and modification.
Amazon, Microsoft, Alphabet, Alibaba, and Facebook currently dominate the hyperscale data center market, which despite a broader downturn, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 3.38% from 2021 to 2026.
4. The Use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Data Centers
Artificial intelligence technology has progressed by leaps and bounds in the last decade, and the data center industry was one of the first to embrace it in day-to-day operations.
Data centers use artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in the following ways:
- Automatically place workloads on the most appropriate server based on the workload's requirements, the availability of resources, and the current utilization of the data center. By ensuring that workloads are always running on optimal resources, AI can improve performance and reduce the overall load on the data center.
- Predict and prevent failures in the data center. By analyzing data from sensors, logs, and other sources, AI and ML algorithms identify patterns and trends that indicate an impending failure and take action to prevent it. This additional failsafe improves the data center's reliability and availability while reducing the need for manual intervention and maintenance.
- Optimize the energy usage of a data center. By analyzing energy consumption and workload patterns, AI and ML algorithms identify opportunities to reduce energy usage by powering down idle servers or adjusting the data center's temperature.
Overall, utilizing AI and ML in data centers will play an increasingly important role in the future of data center management and operations.
5. The Synergy of 5G Networks and Edge Computing
The roll-out of 5G will significantly impact the data center industry by introducing data-hungry technologies that were not previously viable, such as virtual and augmented reality, self-driving cars, remote healthcare, precision farming, and digitized logistics. These technologies are incredibly data-intensive and require specialized infrastructure and software to be used effectively.
Lower latency is also a major requirement for self-driving cars, which rely on it to make split-second decisions and avoid accidents. And as the primary source of latency is distance, more data will have to be processed closer to where it is generated, driving the growth of regional and local data centers.
This is called edge computing, and as the amount of data generated by distributed sources continues to grow, organizations will increasingly have to depend on it instead of centralized data centers.
In anticipation of a further shift towards edge computing and 5G workloads, phoenixNAP is taking Bare Metal Cloud to the edge. Our edge point in Austin, Texas, provides low-latency (10 milliseconds) access to Bare Metal Cloud to the U.S. Southwest.
6. The Rise of Automation
Automation in data centers refers to using technology and software to automate a wide range of tasks and processes in a data center. Automation can include everything from provisioning and managing infrastructure to deploying and scaling applications to monitoring and maintaining the data center.
We can now automate the following everyday data center tasks:
- Monitoring the health and performance of data center components.
- Detecting and responding to potential problems.
- Performing routine maintenance tasks.
- Reducing the need for manual labor.
Central to the automation of data centers is DevOps. This software development methodology combines the traditionally separate roles of development and operations to improve product delivery speed, quality, and efficiency. DevOps relies on automating as many repetitive tasks as possible and incentivizes all parties involved to deliver robust solutions.
We embraced DevOps and never looked back. If you’re curious about how we did it, check out the article by Peter Borg, one of our lead engineers, on the six simple steps of transitioning to a DevOps culture.
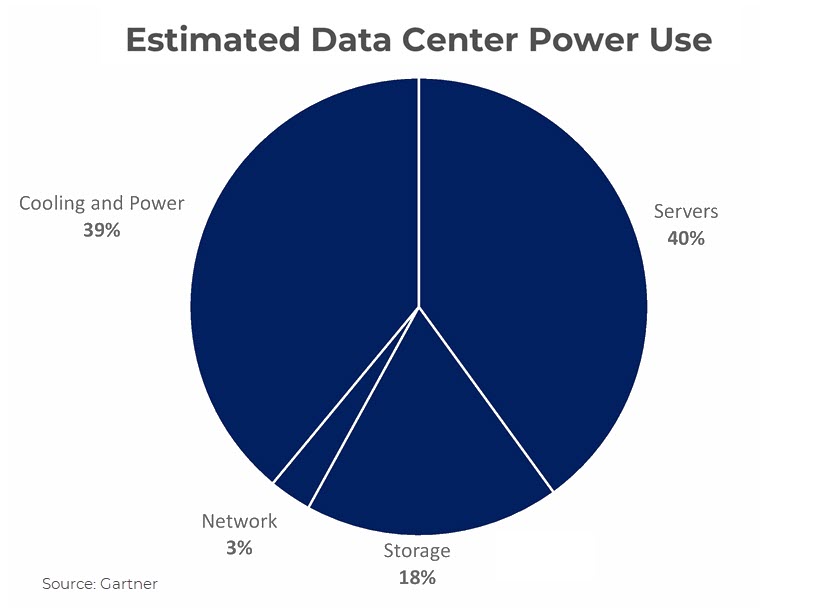
7. The Growing Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As concerns about the environmental impact of data centers grow, the industry is looking for ways to make their data centers sustainable and energy efficient while reducing costs and improving overall performance.
Here is what the data center industry is increasingly focusing on:
- By using energy-efficient hardware and infrastructure, data centers reduce their energy consumption and lower operating costs and carbon footprint.
- Data centers are pivoting to renewable energy sources such as solar or wind. Besides being better for the environment, they also reduce exposure to energy price fluctuations, improving long-term cost predictability.
- Using efficient cooling systems, data centers maintain optimal operating temperatures for hardware, improving reliability and performance.
- Building data centers taller rather than wider saves space and reduces the overall environmental footprint. Additionally, a taller design improves efficiency by allowing for better airflow and cooling, as well as reducing the distance data needs to travel within the data center.
Overall, green technology represents a growing trend in the industry, as more data centers are looking for ways to reduce their environmental impact and improve the sustainability of their operations.
Conclusion
We are witnessing rapid technological advances, from artificial intelligence and machine learning to renewable energy and sustainable design. These advances drive progress in many fields, from healthcare and education to transportation and commerce.
The growth of cloud and edge computing is also making it easier and more affordable for organizations of all sizes to access the computing resources they need.
The increasing use of automation is improving data center efficiency and making it easier to manage and maintain complex IT environments. At the same time, the growth of renewable energy and sustainable design is helping to make technology more environmentally friendly and responsible.
Overall, these are exciting times, and I firmly believe we will see continued innovation in the coming years.




