Introduction
It is essential to know which version of MySQL you have installed.
Knowing the version number helps to determine if a specific feature is available or compatible with your system. This article provides five options to check your version of MySQL on Linux operating systems.
Prerequisites
- Access to the command line/terminal window
- Some operations require sudo or root privileges
- MySQL or MySQL fork installed (forks: MariaDB, Percona Server )
Check MySQL Version with V Command
The easiest way to find the MySQL version is with the command:
mysql -VThe command mysql –V is not OS specific. This command works on Windows, OS X, and Linux distributions including Ubuntu.

The MySQL client version in the example above is 10.4.5-MariaDB.
Note: The command provides the version of the MySQL client utility. The version could be the same as the MySQL server utility if installed on the same system as the server. However, if the client and server utilities are installed on different systems, they might not be the same.
How to Find Version Number with mysql Command
The MySQL command-line client is a simple SQL shell with input editing capabilities. You need to have administrative privileges or use the sudo command to gain access.
To access your MySQL client, use the command:
mysqlMySQL version data is available automatically once the MySQL client loads.
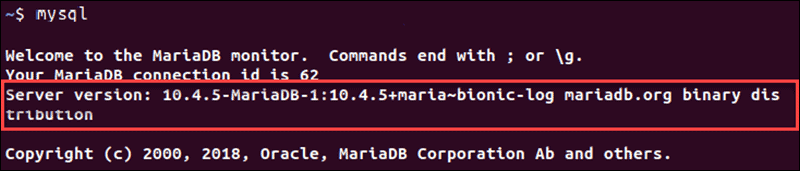
The MySQL client shell offers a lot more options to retrieve detailed information about the version installed.
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE Statement
Now that you have accessed the MySQL client shell, statements can provide detailed information about your MySQL installation. Keep in mind that all text commands within the MySQL client must end with a semicolon “;”
Enter the following command:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘%version%’;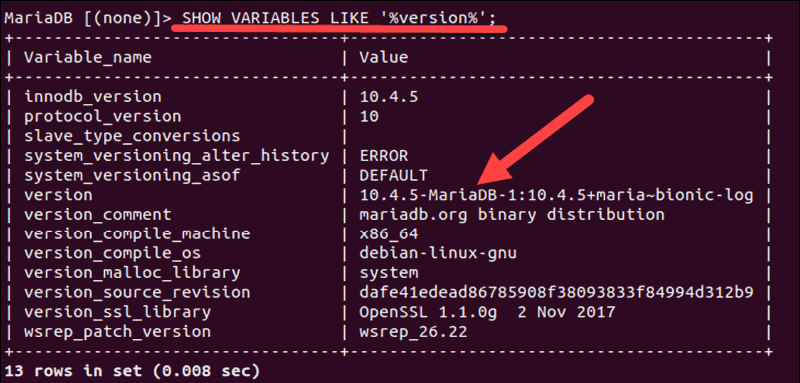
The variable that contains MySQL version information is version.
SELECT VERSION Statement
It’s possible to obtain the version from within the MYSQL client by typing the SELECT VERSION() statement:
SELECT VERSION();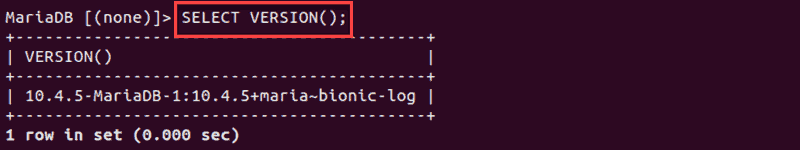
This command derives the data from the version variable disregarding other variables.
STATUS Command
The STATUS command displays the version as well as version comment information:
STATUS;The output includes uptime (how long the MySQL server has been running), threads (the number of active threads), and other useful information.
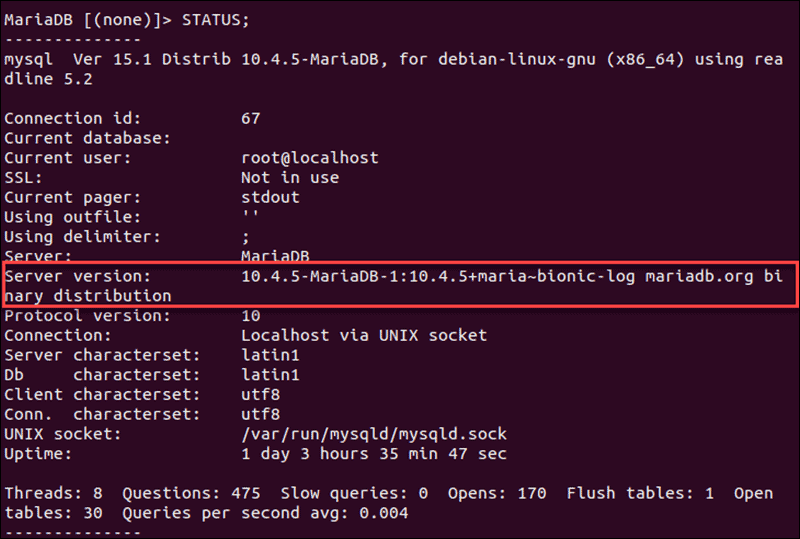
This statement provides the most comprehensive overview regarding the status of the MySQL installation and its current version.
Note: For other operating systems, read our guides Check the MySQL Version on Windows and Check MySQL Version on macOS.
Conclusion
You now know how to use the command line to check your MySQL version. Additionally, if you need to get a more detailed account of your MySQL version, this article explained how to display additional data from within the MySQL client.