Introduction
Jenkins is an open-source software package for continuous software development. It is used to automate parts of the build, testing, delivery, and deployment of applications. Jenkins is based on Java and facilitates every part of the software development process.
This guide will show you how to install Jenkins on CentOS or Rocky Linux.

Prerequisites
- A system running CentOS or Rocky Linux.
- A user account with root privileges.
- Access to a terminal window/command line.
- Java installed.
Step 1: Install Java
Jenkins is a Java-based application that requires the Java Development Kit to be installed on your system. The latest stable Java JDK version available in the repository at the time this article was written is Java OpenJDK 17. If you already have the latest Java version installed and set as the default, skip ahead to Step 2.
Follow the steps below to install Java:
1. Open the terminal and update the system package repository information:
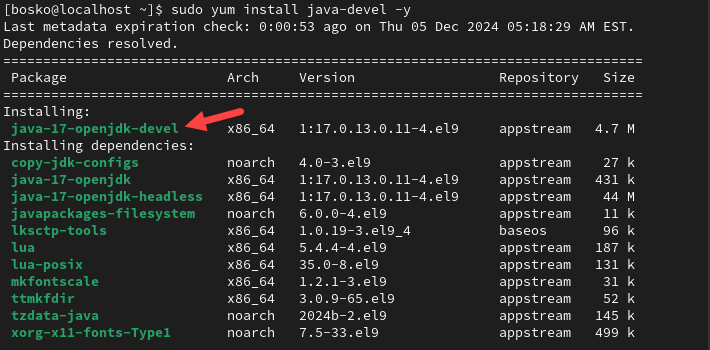
sudo yum update2. Install the latest Java OpenJDK version.
sudo yum install java-devel -yThe system scans the repositories, downloads, and installs the latest stable Java version.
3. Verify that Java installed successfully by checking the program version:
java --version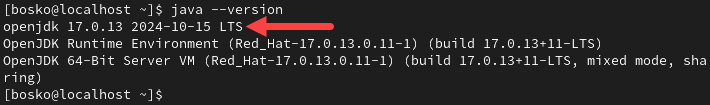
Step 2: Add Jenkins Software Repository
Jenkins is not included in the default CentOS software repositories. Follow the steps below to add the Jenkins repository:
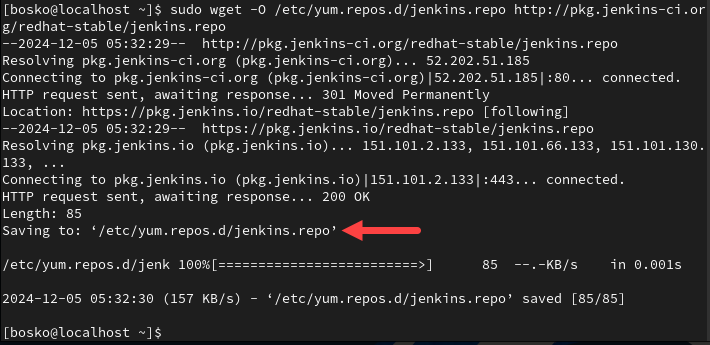
1. Open the terminal and run the command below to add the repository:
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repoThe system reaches out to the Jenkins server and downloads the repository location to your system. The output should be similar to this:
If the repository download fails, you can add it manually. Run the following command to edit the Jenkins repository config file:
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repoPaste the following lines in the file:
[jenkins]
name=Jenkins-stable
baseurl=http://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat
gpgcheck=12. Save the file and exit to apply the changes.
3. Import the GPG key to ensure your software is legitimate:
sudo rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io-2023.keyIf the process is successful, the system returns a new command line without error.
Note: You may have noticed that the repository lists Red Hat, but your system is CentOS or Rocky Linux. This is because they are based on the Red Hat Linux architecture.
Step 3: Install Jenkins on CentOS or Rocky Linux
After adding the repository, install Jenkins with the following command:
sudo yum install jenkins -y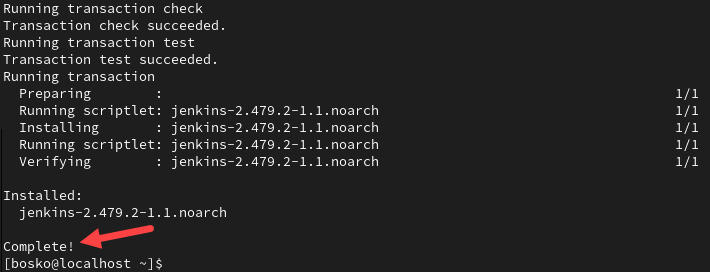
Wait for the process to complete. If you receive an error saying “jenkins not found,” go back and manually add the repository as outlined in the previous step.
Start Jenkins Service
To start the Jenkins service and enable it at startup, run the following commands:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl enable jenkinsCheck the Jenkins service status with:
sudo systemctl status jenkins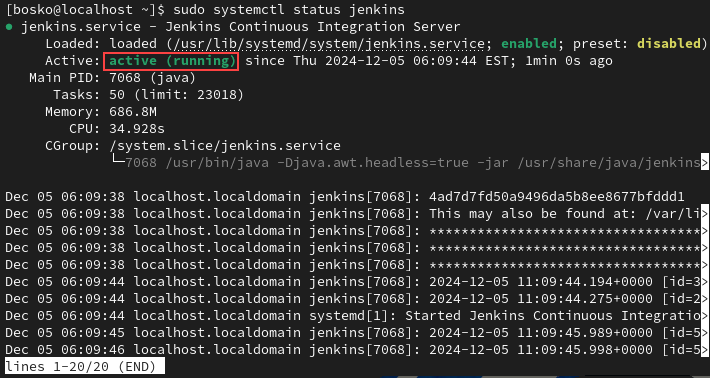
If everything works correctly, the status message should be active (running). Press q to go back to the terminal.
Step 4: Set Firewall to Allow Jenkins
The Jenkins service uses port 8080 to communicate. If you are using the default firewalld service, enter the following commands to allow access:
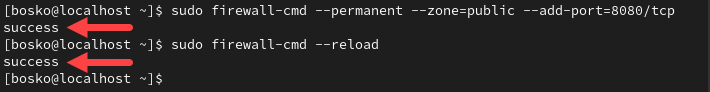
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadThe system reports success for each command:
If you are using a different firewall, follow its instructions to allow TCP traffic on port 8080.
Step 5: Run and Set up Jenkins
Next, we must test the system to ensure Jenkins is working correctly. Follow the steps below:
1. Open a web browser and enter the following URL:
http://localhost:8080If your server is remote or has a specific hostname, domain name, or IP address, use that instead.
The browser should display an Unlock Jenkins page.
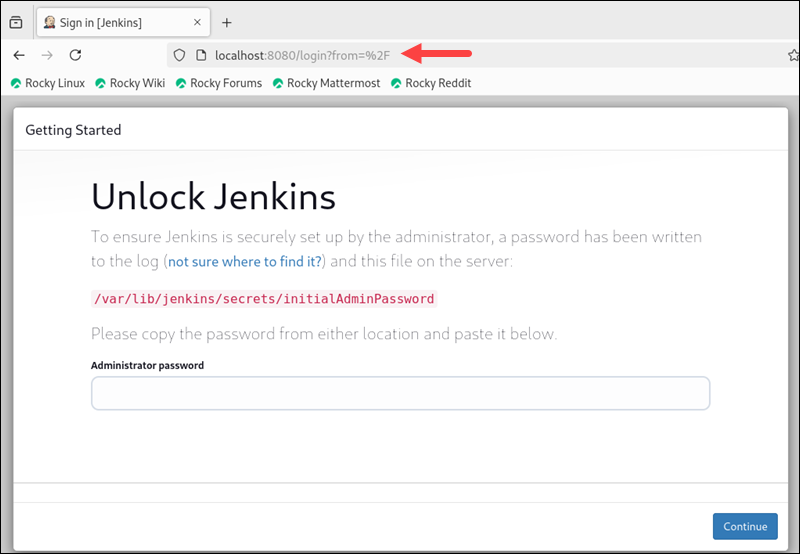
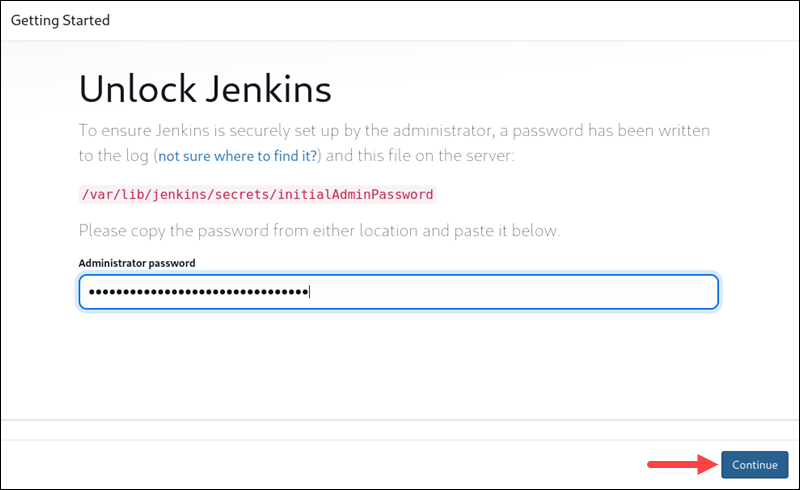
2. The password you need to unlock Jenkins was created automatically (but not displayed) during setup. To find it, switch to a terminal window and enter the following:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordThe location is displayed on the Getting Started / Unlock Jenkins page.
The terminal output displays an alphanumeric code. Copy this code and paste it into the password field. Then click Continue.
3. Jenkins prompts you to install plugins. It is recommended that you Install suggested plugins. You can always change or customize plugins later.
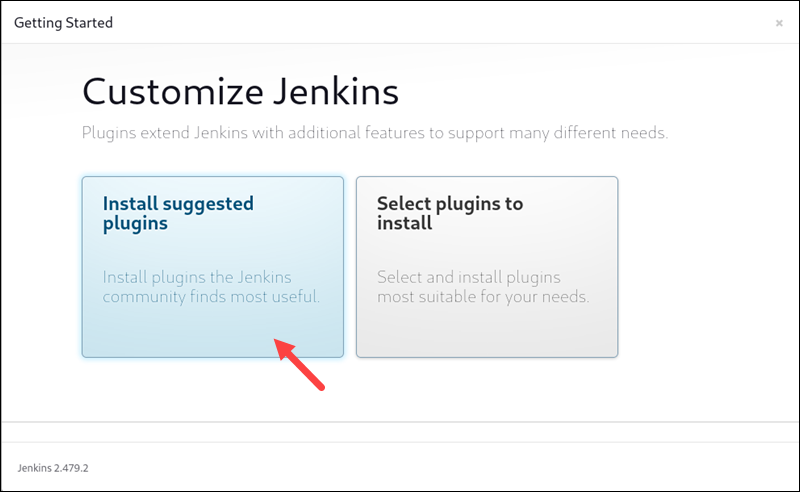
Wait for the process to complete.
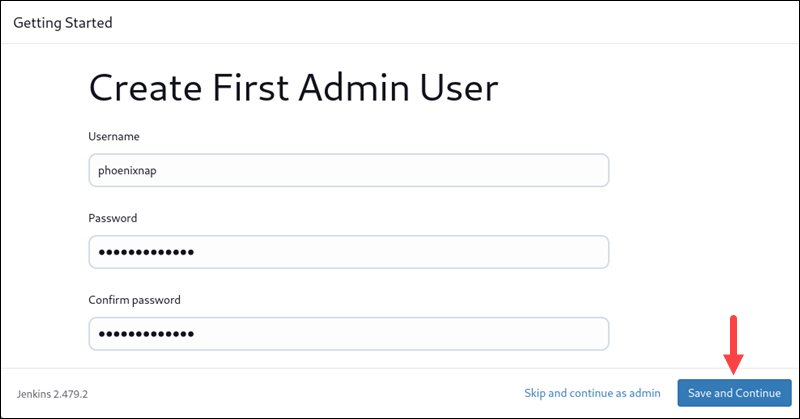
4. Once plugins are configured, create the first Admin user. Enter the required details: username, password, confirm the password, and provide the email you want to use for your Jenkins Admin. Click Save and Continue to continue with the configuration.
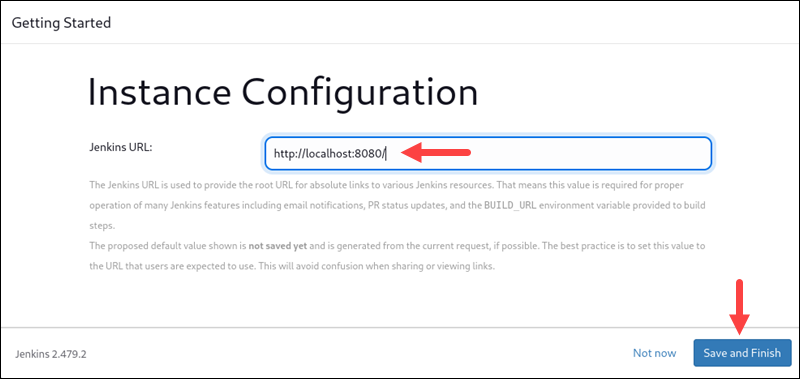
5. The last page allows you to configure the Jenkins instance. This shows the Jenkins hostname. It is usually the same hostname you used to access the Getting Started page. If you do not create an admin user, there will be a warning.
Enter the URL or keep the default one and click Save and Finish to start using Jenkins.
6. After you complete the Jenkins configuration, the Jenkins dashboard appears, where you can create new jobs.
Note: Refer to phoenixNAP's Jenkins tutorial for beginners to learn all you need to know about Jenkins.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to install and configure Jenkins on your CentOS or Rocky Linux system. If you follow the steps in this guide, your Jenkins dashboard should load properly, and you can start creating jobs.
If you are using a different distribution of Linux, we also have a guide on how to install Jenkins on Debian 10, and how to install Jenkins on Ubuntu.