Introduction
Knowing how to unzip a file in Ubuntu allows you to access and use compressed files, saves storage space, and makes transferring and sharing files easier.
Moreover, many software packages are distributed in compressed formats, so being able to unzip files is essential for software installation and system maintenance.
This guide explains how to unzip a file in Ubuntu using one of the two methods.
Prerequisites
- A Linux system (this tutorial uses Ubuntu 22.04).
- Access to the terminal.
- sudo or root privileges.
How to Unzip a ZIP File in Ubuntu
There are two ways to unzip a file in Ubuntu: via the unzip command or GUI (Graphical User Interface). The following text elaborates on both methods.
Unzipping a File in Ubuntu via the unzip Command
The unzip command provides control and flexibility over file extraction. It also allows for the efficient extraction of multiple files simultaneously, making it more suitable for batch operations than a graphical user interface (GUI).
To extract files using unzip, follow these steps.
1. Ubuntu distributions usually include the unzip utility by default. If your machine does not, update the repositories with sudo apt update and use the following command to install unzip:
sudo apt install unzip
2. Locate the file you want to unzip. In this example, the files.zip archive is located in the Home directory. To verify the file is there, run the ls command:
ls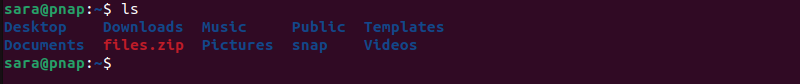
The archive (colored red) is present in the current directory.
Note: In case your archive is not in the current directory, navigate to its location using the cd command.
3. To unzip the files.zip archive, run the following:
unzip files.zip
The system decompresses the file and places a copy of its contents in the current directory.
Unzipping a File in Ubuntu Using the GUI
Another way to unzip an archive is using GUI. For instance, to unzip the files.zip archive, follow these steps:
1. Right-click the archive.
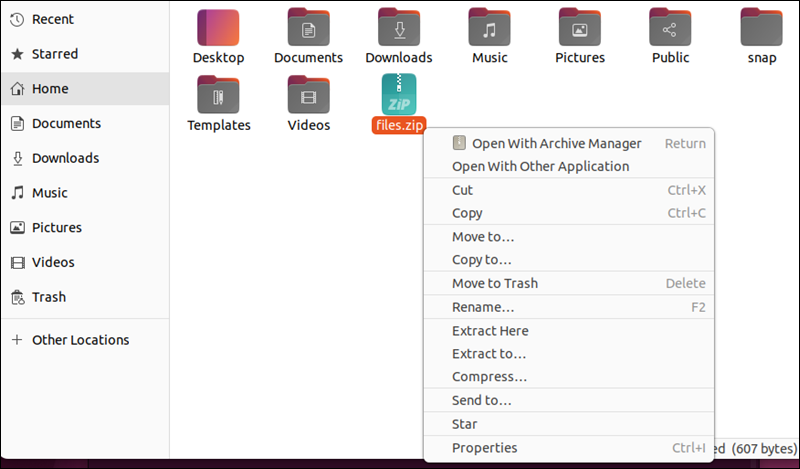
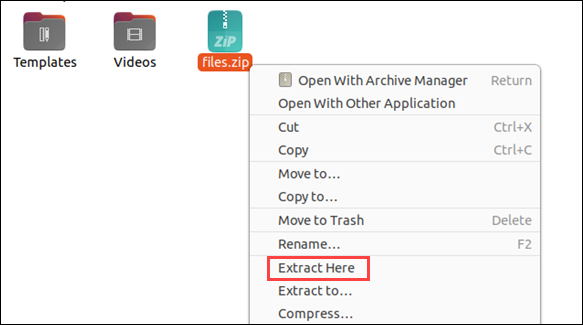
2. Choose Extract Here.
3. Check the current directory to verify the process was successful. The extracted files are placed in the directory with the same name as the archive.
To extract files to a different directory:
1. Choose Extract to... after right-clicking the archive.
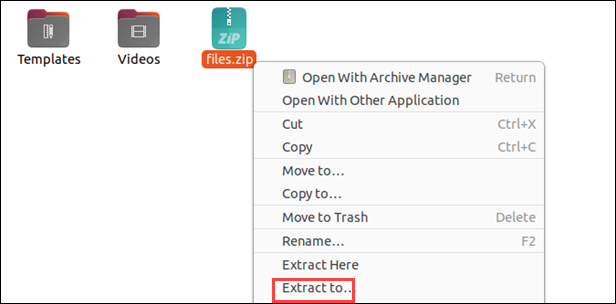
2. Navigate to the location where you want to extract the files. In this example, it's Documents.
3. Click Select.
4. Access the selected directory (in this case, Documents) to confirm files are extracted there.
unzip Command Additional Options and Examples
The unzip command also works with additional options, which provide more control over how it works. The common options are in the table below.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-P | Specifies a password for ZIP archives. |
-t | Tests if the file is valid. |
-j | Extracts files without creating directories for them. |
-x | Excludes a file when unzipping. |
-q | Quiet mode. Suppresses the normal output unzip output. |
-v | Verbose mode. Displays detailed information about the extraction process. |
-l | Lists the ZIP file contents. |
-d | Extracts the file contents to a different directory. |
-o | Overwrites files without prompting. |
The following sections show usage examples of different unzip options.
How to Test a ZIP File is Valid
If you think the zipped file has been damaged or corrupted, use the –t option to test the file. Run the following:
unzip -t [zip-file-name]In this example, we're testing the files.zip file with:
unzip -t files.zip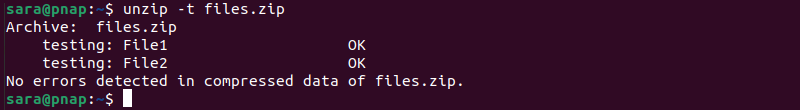
The output confirms the ZIP archive and its contents are intact and without errors.
How to Exclude Files When Unzipping a ZIP File
To exclude a file when extracting files, run the following:
unzip [zip-file-name] –x [file-name]For instance, files.zip contains two files: File1 and File2. To exclude File1 from being extracted, run:
unzip files.zip -x File1
The command only extracts File2.
How to List the Contents of a Zip File
To list ZIP file contents, use the -l option with the zip command. For instance, list files.zip contents with:
unzip -l files.zip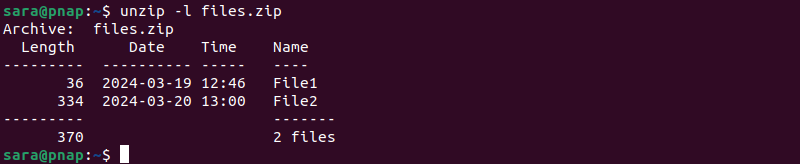
Extract a ZIP File to a Different Directory
To specify you want to unzip to a different destination than the directory you are in, type the command:
unzip [zip-file-name] –d [destination-directory-name]For instance, unzip files.zip to the Documents directory with:
sudo unzip files.zip -d /Documents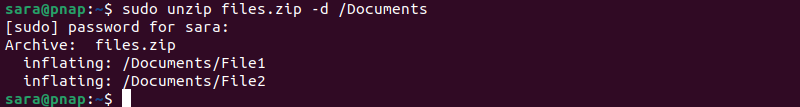
In this example, using the sudo command is necessary because the extraction destination directory /Documents requires administrative privileges.
How to Unzip Multiple ZIP Files
For example, the current directory contains several zipped archives (files, files1, files2).

To unzip all the archives in the current directory, run:
unzip "*.zip"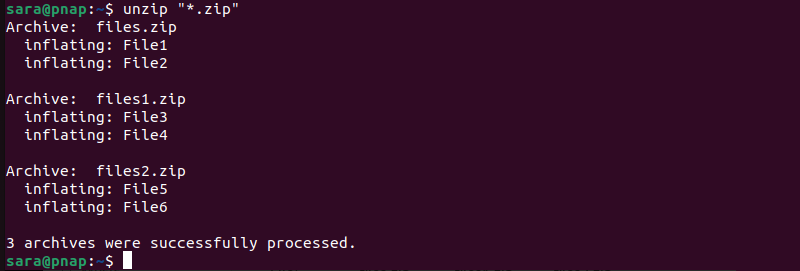
The * sign is a wildcard, which means any number of characters. Therefore, the command finds and unzips any file that ends in .zip.
Conclusion
This article explained how to unzip a ZIP file in Ubuntu via the terminal or GUI. Refer to the provided examples to test how the command works.
Next, learn how to zip a file in Linux.

