IT departments worldwide rely on the cloud to streamline operations and free up resources for core business goals. Cloud adoption is widespread, and for many organizations, it is not a question of "if" but "how" to leverage the cloud effectively.
Cloud computing has evolved to offer flexibility in deployment and service. There are three main models: public clouds (owned by a cloud provider), private clouds (dedicated to a single organization), and hybrid clouds (combining both).
This article compares public and private clouds, the most popular deployment models, to help you reach a decision that will benefit your organization’s critical business objectives.
What Is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a computing model that offers a proprietary IT environment dedicated to a single business entity. Unlike public clouds, which provide services to multiple organizations, a private cloud delivers similar scalability and self-service but through a privately-operated architecture.
How Does a Private Cloud Work?
A private cloud uses software and hardware to create a dedicated cloud environment exclusively for one organization. This environment can be hosted on-premises, in a company's own data center, or off-premises by a third-party provider.
The key components of a private cloud infrastructure include computing resources (servers), IT storage systems, and networking equipment, all managed via a virtualization layer. Virtualization creates multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, maximizing resource use. Additionally, management tools give administrators control over the cloud, including allocating resources, managing security policies, and monitoring performance and resource utilization.
Private Cloud Advantages and Use Cases
The private cloud model offers distinct advantages. Here is an overview of the use cases and benefits:
- Regulatory compliance and data privacy. Private clouds provide control and security in data handling. The enhanced privacy is particularly relevant in highly regulated sectors like finance and healthcare, where adhering to standards like PCI DSS and HIPAA is mandatory.
- Customization and flexibility. Private clouds offer a highly customizable IT infrastructure. This adaptability allows organizations to tailor their computing environment to their operational needs, optimizing performance and efficiency.
- Predictable workloads and cost-effectiveness. Private clouds are cost-effective for organizations with consistent and predictable computing demands.
- Enhanced security. Beyond compliance, private clouds offer superior security features. Dedicated resources and isolated environments give organizations greater control over their data, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- High performance. Private clouds offer dedicated computing resources, guaranteeing high performance and availability. This performance boost is crucial for mission-critical applications and services that require consistent and reliable computing power.
Private Cloud Disadvantages
Despite the advantages, private clouds come with several challenges and drawbacks.
- Higher initial costs. Setting up a private cloud involves significant upfront investment in infrastructure and software.
- Maintenance and management. A private cloud requires a dedicated IT team to manage and maintain it.
- Limited scalability. The scalability of a private cloud is limited by the physical infrastructure of the data center hosting it.
- Complexity. Implementing and managing a private cloud requires specialized skills and knowledge.
Private Cloud Costs
Private clouds are generally more expensive than public clouds. With a private cloud, you are responsible for all the infrastructure and staff management. However, you can offset some of the costs if your organization has consistent resource needs and the expertise to manage the cloud effectively.
Key cost components include:
- Capital expenditure (CapEx). Includes the costs of physical hardware, network infrastructure, and data center facilities if hosted on-premises.
- Operational expenditure (OpEx). Covers ongoing costs such as software licenses, support services, and the salaries of IT staff managing the cloud.
- Utility costs. Data center power and cooling are significant ongoing costs for on-premises deployments.
Our in-depth article explains the difference between CapEx and OpEx. Understanding when to use each payment model is critical to making intelligent financial decisions, optimizing your budget, and maximizing your return on investment.
What Is a Public Cloud?
A public cloud is a cloud computing model in which computing services are offered over the internet by cloud service providers. These services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence.
The infrastructure and services in a public cloud are owned and operated by the cloud provider, and resources are shared among multiple customers. This is known as the "multi-tenant" model. Individuals, startups, and businesses of all sizes can leverage public cloud services.
How Does a Public Cloud Work?
Public clouds deliver a range of services hosted on the provider's infrastructure, eliminating the need for organizations and individuals to invest in and maintain their own physical servers and data centers.
Users access services via a web browser or API, and resources are provisioned dynamically based on demand. The underlying technology includes virtualization, which enables efficient resource allocation and scaling.
Leading public cloud providers use globally distributed hyperscale data centers to maintain reliability, performance, and high availability.
Public Cloud Advantages and Use Cases
Public clouds offer significant advantages catering to a wide range of business needs.
- Scalability and rapid adaptation. Public clouds can seamlessly accommodate fluctuating demands, enabling businesses to scale resources up or down efficiently. The scalability of the public cloud is especially beneficial for organizations dealing with unpredictable workloads.
- Financial flexibility. The public cloud's pay-as-you-go pricing model reduces the need for upfront capital investments, providing the financial flexibility needed for growth and innovation.
- Global service delivery. Leading public cloud providers leverage a vast infrastructure network to facilitate global reach, ensuring reduced latency and improved performance across dispersed geographic locations. This factor is vital for organizations seeking to expand their footprint internationally.
- Innovation and speed to market. The public cloud offers a platform that supports rapid testing and deployment of new applications, significantly reducing the time and investment required to bring new products to the market.
- Maintenance and operational efficiency. By outsourcing infrastructure maintenance and upgrades to the cloud provider, companies can redirect their IT efforts toward strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced reliability. With a robust network of data centers ensuring high uptime and reliability, public clouds provide business continuity safeguards, including data backup and disaster recovery mechanisms.
Moving your data and operations to the cloud is not a magic bullet. Hardware failures, data breaches, and software bugs also happen in cloud environments.
To make better decisions for your business, read our CEO's article on the opportunities and challenges of business continuity in the cloud.
Public Cloud Disadvantages
Despite its numerous advantages, the public cloud is not without drawbacks.
- Security and privacy concerns. Sharing resources with other organizations raises concerns about data security and privacy, even though providers invest heavily in cloud security.
- Compliance challenges. Meeting regulatory compliance is more complicated in a public cloud environment. For instance, if you store the personal data of EU citizens, you will need to ensure the cloud provider is GDPR compliant.
- Limited control. Users have less control over the infrastructure and operational environment than with private clouds, which may be an issue for some applications.
- Potential for unexpected costs. While pay-as-you-go is generally cost-effective, it can lead to unexpected expenditures if you don’t carefully monitor and manage usage.
Read our guide on cloud computing costs to ensure you're never caught off guard by a confusing cloud bill.
Public Cloud Costs
Public cloud deployments are generally more affordable than private clouds because it isn’t necessary to invest in hardware or manage a data center. Additionally, cloud providers benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to offer competitive pricing.
However, if your company deals with massive datasets, cloud costs can spiral. In cases like these, a private cloud might be the more economical option.
Here are the factors that influence public cloud costs:
- Service type. The nature of the services (computing, storage, database) and configurations significantly affect costs. For example, low-powered virtual machines with HDD storage are much more affordable than high-performance machines with SSD storage.
- Resource consumption. Public clouds typically follow a pay-as-you-go model, meaning customers are billed based on resource usage. Subsequently, costs vary greatly depending on CPU hours, storage space, and consumed bandwidth.
- Pricing models. Providers offer various pricing models, including on-demand pricing, reserved instances, and spot pricing, each with distinct implications.
- Additional services. Advanced features such as automated scaling, monitoring, and security services will likely incur additional fees.
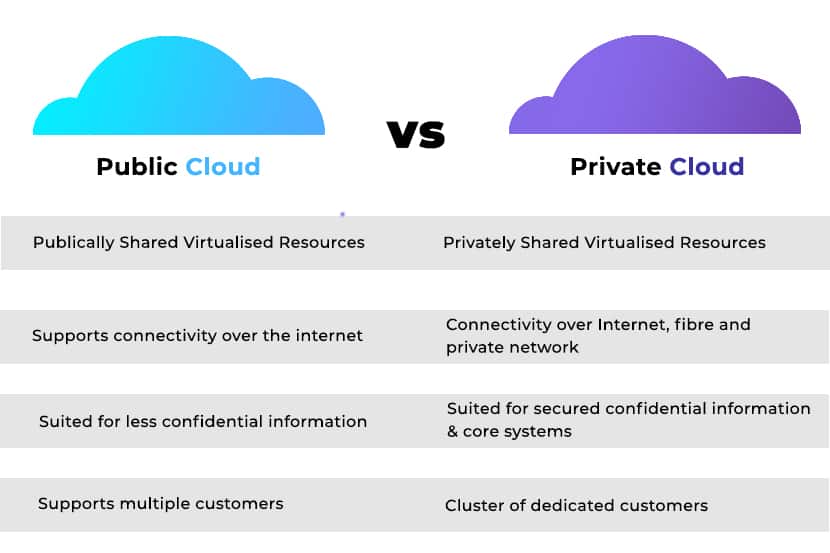
Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud: Comparison
Here is a chart comparing the key features of public and private cloud deployments.
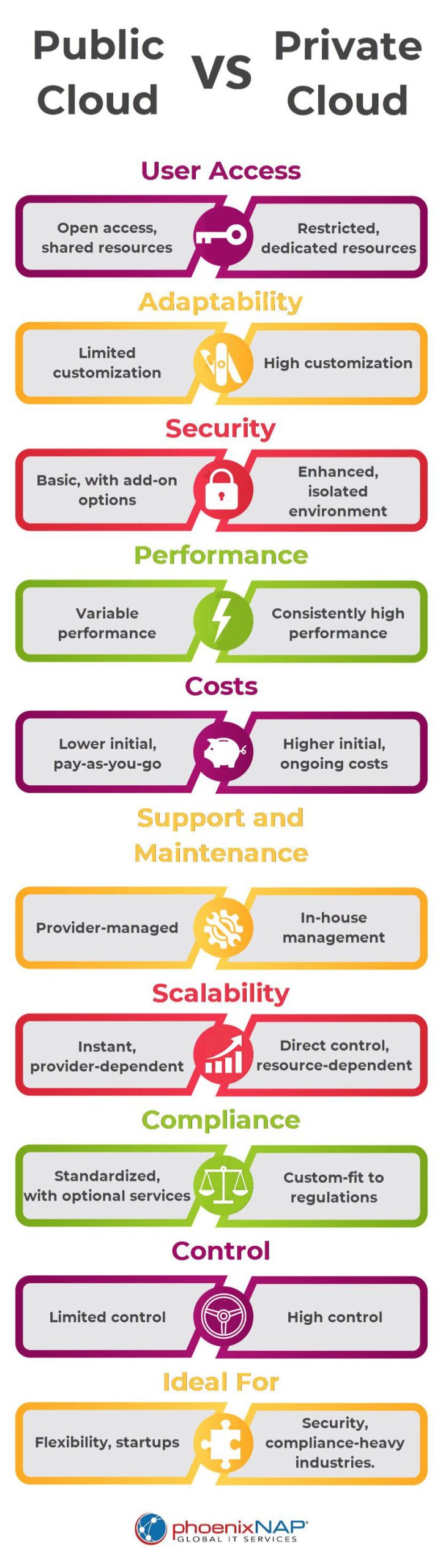
| Point of comparison | Public cloud | Private cloud |
|---|---|---|
| User access | Accessible to the public, with shared resources among users. | Restricted to authorized users, offering dedicated resources per client. |
| Adaptability | Limited customization due to shared resources. | High customization and adaptability to meet specific client requirements. |
| Security | Basic security is provided, with options for additional features. | Enhanced security and isolation, better suited for meeting data protection standards. |
| High performance | Potential performance inconsistency due to shared resources. | Dedicated resources ensure consistently high performance. |
| Costs involved | Lower initial costs with pay-as-you-go pricing. Additional costs for extra services. | Higher initial and ongoing costs due to dedicated infrastructure and staffing needs. |
| Support and maintenance | Managed by the cloud provider, reducing the IT burden on the client. | Typically managed in-house, requiring a dedicated IT team. |
| Scalability | Instant scalability is provided by the cloud provider, though subject to the terms of the service level agreement. | Direct control over scalability, often requiring additional in-house resources or infrastructure changes. |
| Compliance | May offer standardized compliance solutions, potentially requiring additional services for specific needs. | Can be tailored to meet specific regulatory compliance requirements more directly. |
| Control | Less control over the computing environment and underlying infrastructure. | Greater control over the computing environment, allowing for specific configurations and setups. |
| Ideal for | Ideal for businesses needing flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs. Suitable for startups, testing, and development environments. | Best for organizations requiring stringent security, compliance, and high performance for critical applications. |
Are you struggling to balance security, performance, and control in the cloud? Public cloud solutions offer ease of use but often lack the customization and isolation needed for sensitive data. An on-premises infrastructure provides ultimate control but managing it can be a burden.
phoenixNAP's Managed Private Cloud bridges the gap. It delivers a dedicated cloud environment built to your exact specifications, with the added benefit of expert management by our team.
The Rise of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
A transformative trend is taking center stage when discussing cloud options: the strategic use of multiple cloud environments. Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud offer distinct advantages and cater to unique needs.
Multi-cloud environments distribute workloads across multiple public clouds, leveraging each provider's strengths. By aligning workloads with the most suitable cloud, multi-cloud adoption enhances disaster recovery, avoids vendor lock-in, and facilitates compliance.
On the other hand, hybrid clouds integrate public cloud services with an organization's private cloud. This approach is ideal for organizations with workloads that require on-premises control, as it also allows them to leverage the scalability and cost-efficiency of public clouds for other workloads.
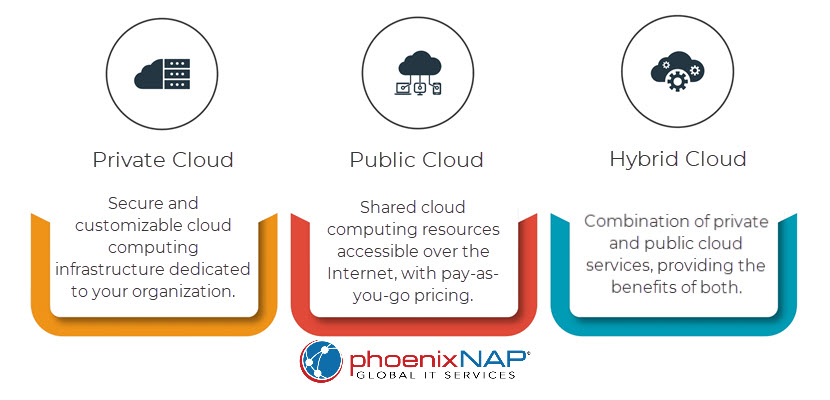
As an alternative cloud provider, phoenixNAP helps you avoid the ever-increasing service costs, suboptimal performance, and management complexity of the public cloud. Explore our offerings and select a service optimized for your workload or mix and match different ones to build the perfect hybrid environment.
Private vs. Public Cloud: Infographic
Here is an infographic that highlights the key distinctions between Private and Public Clouds.
Crafting a Future-Proof Cloud Strategy
After examining the private versus public cloud paradigms, it becomes clear that deciding between the two is not merely a matter of choosing the right technology but also aligning your organization’s broader business coals with the capabilities and constraints of these two options.
As cloud technologies, such as edge computing, hybrid solutions, and serverless computing, advance, organizations have to develop their capacity to adapt to the rapidly changing digital landscape. By staying informed and flexible, businesses ensure their cloud strategy supports long-term growth, innovation, and resilience.



