Introduction
MegaCLI is a tool used as a command-line interface to communicate with the LSI family of RAID controllers. It manages and reports on MegaRAID SAS cards.
In this article, you will learn how to install MegaCLI and set up a hardware RAID.
Prerequisites
- A Linux system (installation instructions apply to CentOS/RHEL and Ubuntu based distros)
- Access to the command-line/terminal window
- A MegaRAID hardware controller
- An unzip utility tool
Install and Set Up MegaCLI
MegaCLI supports MS Windows, FreeBSD, Solaris and all major Linux distributions. This article provides instructions on installing MegaCLI on CentOS 8 and Ubuntu.
Step 1: Verify Your Hardware RAID Controller
To use MegaCLI, you need a MegaRAID SAS controller. If you are unsure which RAID controller you are using, start by verifying it.
Use the lspci command to verify the RAID controller on your system.
lspci | grep -i raidThe output will display your RAID controller. See the example outputs below:
output 1
LSI Logic / Symbios Logic MegaRAID SAS 1078 (rev 04)output 2
01:00.0 RAID bus controller: Adaptec AAC-RAID (rev 09)output 3
02:00.0 RAID bus controller: LSI Logic / Symbios Logic MegaRAID SAS 2208 [Thunderbolt] (rev 05)If you do not receive any output, like in the image below, it is an indication that the system is not identifying any RAID controller. Make sure that the controller is set up correctly.

If the output indicates that you indeed have a MegaRAID SAS controller, move on to installing MegaCLI.
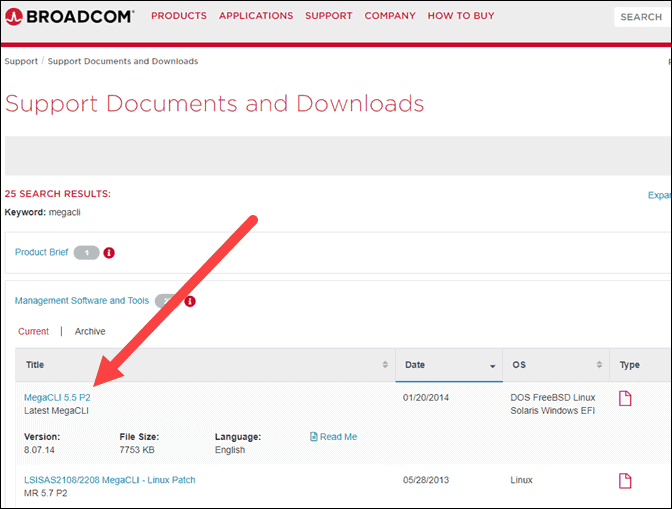
Step 2: Download MegaCLI
Download MegaCLI by navigating to the Support Documents and Downloads section of the Broadcom website. The MegaCLI install file is under the Management Software and Tools list as shown below.
Step 3: Extract the MegaCLI Package
Next, move into the Downloads folder.
cd Downloads3. Extract the 8-07-14_MegaCLI.zip file.
unzip 8-07-14_MegaCLI.zip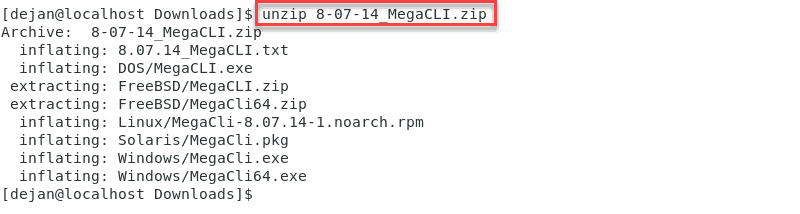
Step 4: Install MegaCLI
Option 1: Install MegaCLI on CentOS 8
Move into the Downloads/Linux folder by typing:
cd Downloads/LinuxOnce in the Linux folder, run the following command to install MegaCLI on CentOS 8:
yum localinstall MegaCli-8.07.14-1.noarch.rpm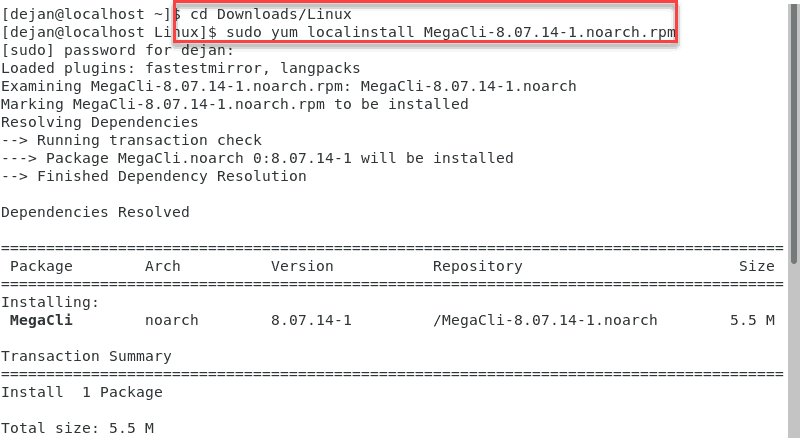
Option 2: Install MegaCLI on Ubuntu
LSI distributes MegaCLI as an rpm package. Ubuntu does not support rpm packages, but the MegaCLI install package can be converted for use with Ubuntu by using Alien.
Start by moving into the Downloads/Linux folder.
cd Downloads/LinuxConvert the MegaCLI rpm package with Alien:
alien -k --scripts MegaCli-8.07.14-1.noarch.rpm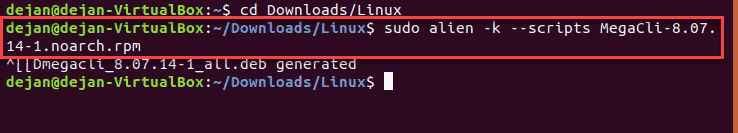
Install the newly created .deb file with the dpkg command:
dpkg -i megacli_8.07.08-1_all.deb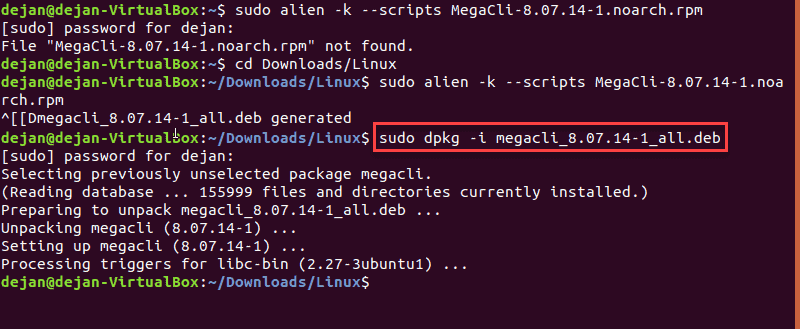
Note: If you don’t have Alien on your Ubuntu system, run the following command to install it:
sudo apt-get install alien
Step 5: Create an Alias
Finally, create an alias for easier reference in the future:
alias megacli='/opt/MegaRAID/MegaCli/MegaCli64'Now that you have MegaCLI set up, examine the list of common commands you will be using to manage RAID disks.
Hardware RAID Setup with MegaCLI
MegaCLI supports configuring all widely used hardware RAID levels:
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10
- RAID 1 with CacheCade
Note: The three basic techniques of RAID levels are disk striping, disk mirroring, and parity. Depending on how these techniques are implemented, different RAID types and levels can be established. To learn more, check out our article on RAID levels and types.
Clear Configuration
Before you configure any disks, make sure to delete any previous configuration you may have on them. The following commands will allow you to do so:
megacli -CacheCade -remove -LALL -aALLmegacli -CfgCacheCadeDel -LALL -aALLmegacli -CfgLdDel -LAll -aAllmegacli -CfgClr -force -aAllConfigure RAID 0
To configure disks as RAID 0 which will strip data across two or more disks, use the commands:
megacli -CfgEachDskRaid0 -a0megacli -LDInfo -LAll -a0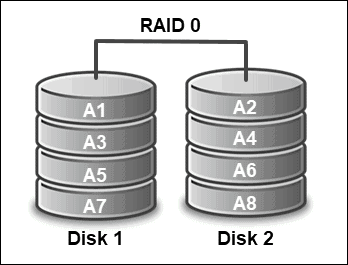
Configure RAID 1
To configure a RAID 1 setup of two disks from slot 0 to 1, type:
megacli -CfgLdAdd -r1 [252:0,252:1] -a0megacli -LDInfo -LAll -a0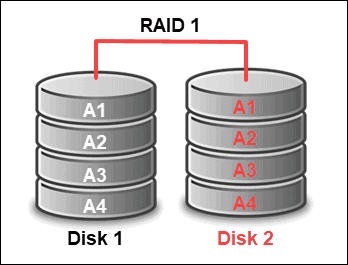
Configure RAID 5
To configure a RAID 5 device made up of disks from slots 0 to 5 use the command:
megacli -CfgLdAdd -r5 [252:0,252:1,252:2,252:3,252:4,252:5] -a0megacli -LDInfo -LAll -a0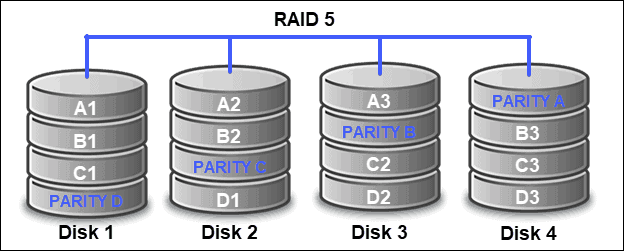
Configure RAID 10
To configure RAID 10 consisting of 8 disks placed in slots 0 to 7, type:
megacli -CfgSpanAdd -r10 -Array0[252:0,252:1] -Array1[252:2,252:3] -Array2[252:4,252:5] -Array2[252:6,252:7] -a0megacli -LDInfo -LAll -a0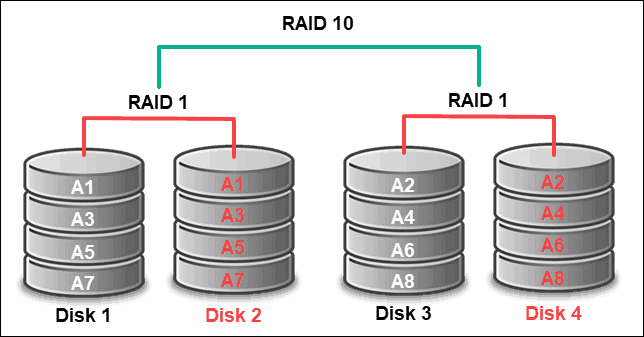
Configure RAID with CacheCade
You can also create additional CacheCade in RAID 1 on SSD disks.
For example, if you have 6 disks in slots 0 through 5. You can create a RAID 5 device consisting of four disks and an additional CacheCade on the remaining two disks.
1. Configure RAID 5 on disks 0 through 4 with the command:
megacli -CfgLdAdd -r5 [252:0,252:1,252:2,252:3,252:4] -a02. Next, create CacheCade configuration using SSDs for slots 5 and 6:
megacli -CfgCacheCadeAdd -r1 -Physdrv[252:5,252:6] WB -assign -L0 -a0Check Adapter, Device Status and Configuration
There are several commands you can use to check the status of your adapters and RAID devices.
To see details of all adapters use:
megacli -AdpAllInfo -aAllTo see status and configuration of all logical drives:
megacli -LDInfo -LAll -aAllTo show information of all physical disks use:
megacli -PDList –aAllFor enclosure information type:
megacli -EncInfo -aALLConclusion
After reading this article you should now be more informed on how to install and use MegaCLI to effectively manage your RAID devices and configurations.