Introduction
Managing files and directories is one of the most basic tasks when working in a Linux system. You can move directories in Linux using the GUI and system commands.
In this tutorial, we will cover the two methods you can use to move directories in Linux.

Prerequisites
- A system running a Linux distribution
- An account with sudo privileges
- Access to the terminal window/command line
How to Use mv Command to Move Directories in Linux
The mv command is a Linux system utility that allows you to move files and directories from one place to another. It uses the following command syntax:
mv [options] [source] [destination]For instance, to move the Example directory to the Downloads directory use:
mv Example DownloadsThere will be no output if the command has been successful.
Moving multiple directories works by changing the syntax to include multiple sources:
mv [source 1] [source 2] … [source n] [destination]For example, to move the Example1, Example2, and Example3 directories to the Downloads directory use:
mv Example1 Example2 Example3 DownloadsNote: Learn how to create new directories in Linux using the terminal in our guide to the Linux mkdir command.
The mv command is also used to rename files and directories with the following syntax:
mv [old filename] [new filename]For example, renaming the Example file into Test:
mv Example TestNote: If the destination directory does not exist, the mv command will automatically rename the source directory to the destination name.
mv Command Options
The mv command uses the following options:
--backup: Creates a backup of the destination file. Allows you to pass additional arguments to change how the command behaves.-b: Works like--backupbut does not accept arguments.-f: Automatically overwrite destination files.-i: Enables interactive mode, with a prompt asking for input before overwriting files.-n: Disables overwriting destination files.--strip-trailing-slashes: Removes trailing slashes ("/") from source file or directory names.-S: Provide a new suffix for the backup files.-t: Move all provided sources into a destination directory.-T: Treat the provided destination as a file instead of a directory.-u: Update destination files.-v: Show command output in verbose format.-Z: Set the destination file security context to default.
If the destination file already exists, using the -b option allows you to create a backup of the existing file:
mv -b test.txt ExampleIn this example, the mv command creates a backup of the existing test.txt file in the Example directory before overwriting. The backup file has the same name as the original, with a tilde ("~") added to the end. Use the ls command to verify the backup file:
ls Example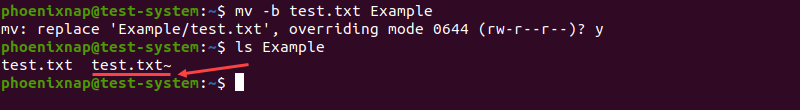
Change the default suffix for backup files (tilde) by combining the --backup and -S options. The new suffix is passed as an argument after the -S option and before specifying the source and destination files or directories:
mv --backup -S 01 test.txt ExampleIn this example, the new backup filename suffix is <em>01</em>:
ls Example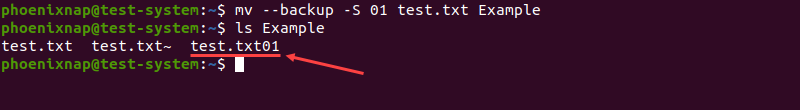
Using the -i option prompts the user to confirm overwriting existing files. Typing Y or N and pressing Enter confirms or cancels overwriting, respectively:
mv -i test.txt Example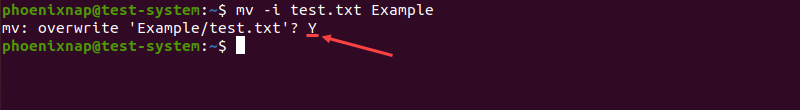
The -f option automatically overwrites any existing files in the destination directory, while the -n option disables overwriting and skips existing files. Using the -u option only overwrites the file if the source file is newer than the destination file of the same name.
Have the mv command output show the step-by-step process of moving files and directories by using the -v option:
mv -v test01.txt test02.txt test03.txt Example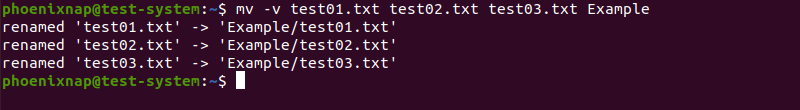
Note: Be careful not to move a directory or file to /dev/null also known as "the black hole". We outline this and other dangerous terminal commands in our article 14 Dangerous Linux Terminal Commands.
How to Move Directories Using GUI in Linux
There are two methods of moving directories in Linux using the GUI.
Option 1: Copy and Paste
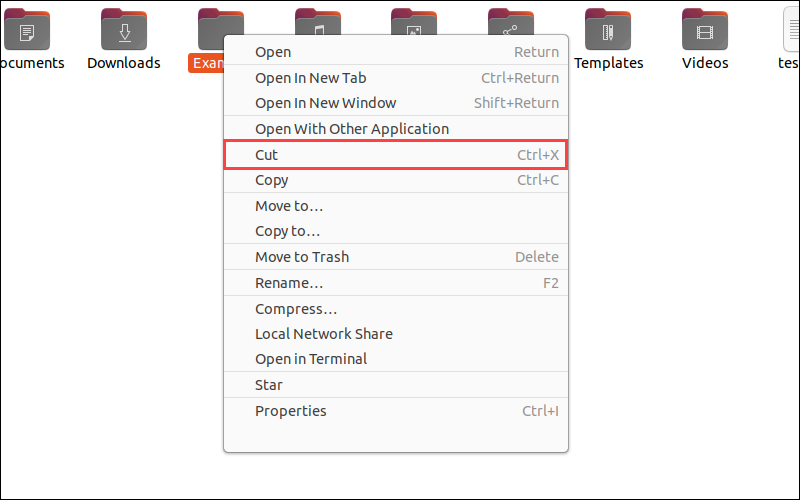
1. Select the directory you want to move and press Ctrl+X. Alternatively, right-click the directory and select Cut from the drop-down menu.
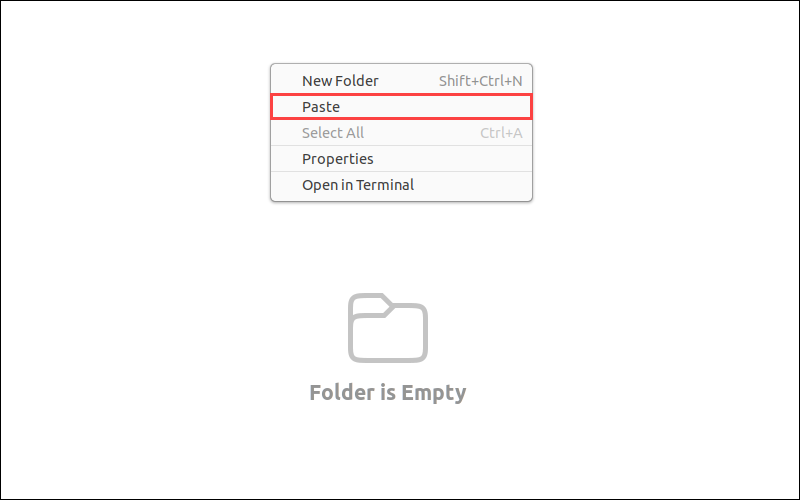
2. Navigate to the destination and press Ctrl+V or right-click the empty space and select Paste from the drop-down menu to move the directory.
Option 2: Move To... Option
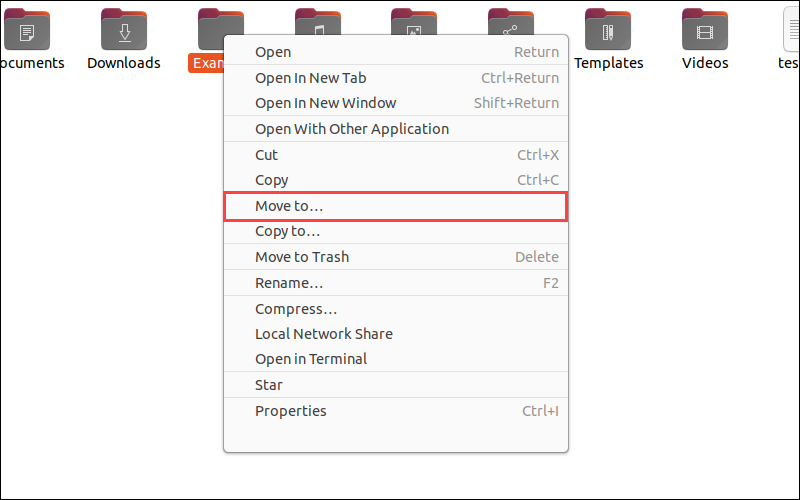
1. Another method is to right-click the directory and select Move to… from the drop-down menu.
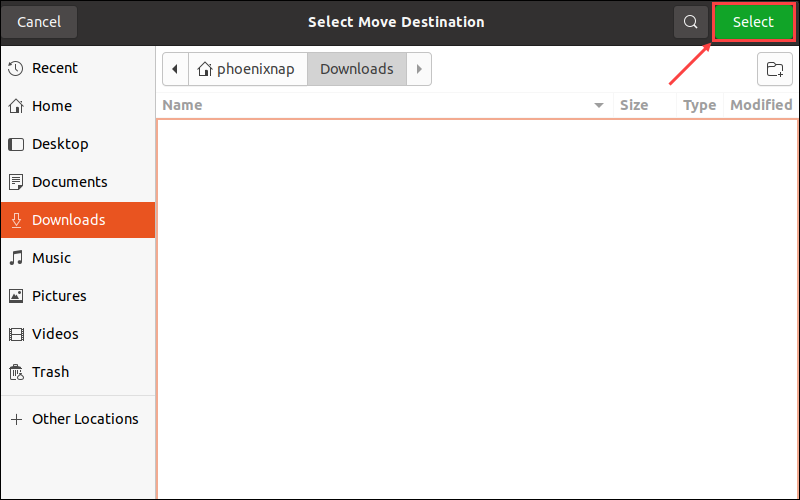
2. In the Select Move Destination window, navigate to the destination and click Select to move the directory.
Note: If you are using Ubuntu, check out our tutorial on how to install a GUI on Ubuntu.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you should know how to move directories in Linux using the GUI and the built-in mv command.
Learn more about using Linux commands in our comprehensive overview of Linux Commands.
For more information about Linux directories, make sure to read our article how to rename a directory in Linux.