Introduction
The purpose of backup and replication is to prevent a catastrophic loss of data due to unforeseen events. Whether it is a natural disaster, failure of underlying hardware, or malicious software, you need to have a fully formed backup strategy.
Deciding what sort of disaster recovery setup you need is the first and possibly the most important aspect of securing and preserving your data. But do you know the difference between backup and replication?
This brief article explores the differences between backup and replication.
Difference Between Backup and Replication
An overview of the differences between backup and replication only seems to emphasize why they are, in fact, complementary rather than opposite options.
| Backup | Replication | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low-cost when compared to Replication. Does not call for significant staff or infrastructure investment. | More expensive than Backup. Off the shelf commercial platforms and solutions can help reduce costs. |
| Requirements | A local disk, virtual tape library, or online backup service. Discretionary storage for archived data. | Implementation of new business processes, additional staff, and investment in infrastructure. |
| Ideal for | Long-term data storage and compliance-related requirements. | Ensuring continuous access to mission-critical and customer-facing applications. |
| Benefits | - Simple to implement. - High level of isolation from potential threats. - Inexpensive. | - Focus on disaster recovery. - High Availability. - A quick resumption of business operations after an outage. |
| Shortcomings | - The considerable time-span between backups. - Long data recovery process. | - Expensive to maintain (especially for long-term storage). - Malicious software can spread to replicated data. |
Note: To illustrate the gravity of data loss, we compiled 2020 Disaster Recovery Statistics.
What is a Data Backup?
Other than using reliable hardware, Data Backup is one of the primary instruments for data recovery. Modern backup systems usually save the state of an entire system and do so at regular intervals. This saved copy can then be safely kept offsite and used to restore the original data if anything happens to the primary location. You simply revert to the most recent copy and save valuable information that would otherwise be irreversibly lost.
Data Backup is ideal for storing large sets of static data for prolonged periods. It is the go-to solution for many industries that are required to maintain reliable long-term records. There are several different types of data backup, usually depending on the amount of data that needs to be stored and the capacity of available resources.
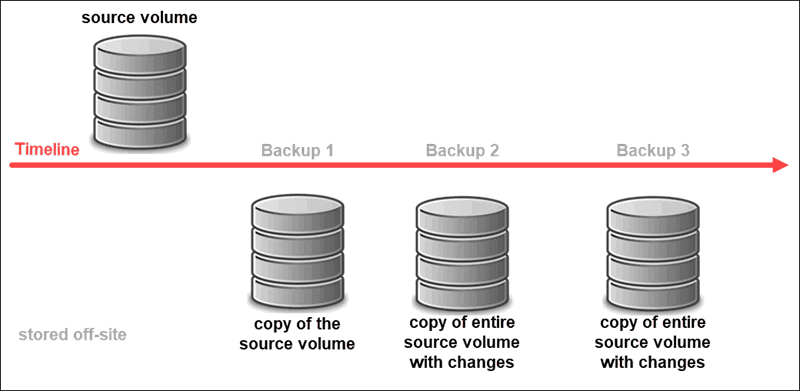
Backing up an entire system can be a burden on resources and is not performed every minute of every day. This means that the most recent copy is often several hours or even several days old. Losing a small amount of data is perfectly acceptable for some businesses, but nowadays, users expect full data consistency and high availability.
The time it takes to retrieve the most recent version and deploy it in a working environment is a severe drawback. Your system would remain unavailable for users until you manage to recover and deploy the copy. Some of these weak points can be reinforced with Data Replication.
What is Data Replication?
Data Replication is a broad term used for technologies and processes that create copies of data, synchronize, and distribute it across a network of servers and data centers. A disaster has minimal impact on data access due to the number of replicas. The system’s availability is extremely high, and the recovery process can usually be measured in minutes. Data Replication, in many ways, solves most of the drawbacks of data backup.
So why do businesses still use both? Replicas are updated all the time and therefore lose the historical state rapidly. If you only use data replication, you would need an immense parallel system to support the replicated data, especially if you need to maintain long term records.
Data Replication can be severely hampered by malware. As data is replicated throughout an entire system, malware can be replicated as well. Without an adequate backup, it might be impossible to revert to a state free of malicious software.
That is why most service providers offer both replication and backup solutions to maintain long term consistency and high availability.
Note: Learn more about the backups in our comparison article Backup vs Disaster Recovery. And to learn more about these two models working together, check out our Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) Guide.
Conclusion
You now have an in-depth understanding of some of the essential aspects of Backup and Replication.
Try to accumulate a lot of impartial and well-rounded information about Data Recovery. The groundwork you lay in this respect can save you a lot of time and effort in case of emergencies.