Introduction
The new norm of working from home brought new vocabulary such as VPN and VDI in our everyday lives. If you are a businesses owner or administrator that had to start thinking about establishing new systems to enable your employees to work from home safely, you most likely came across these terms.
Learn more about the difference between VPN and VDI to find out which one would be better for you.

What is VPN?
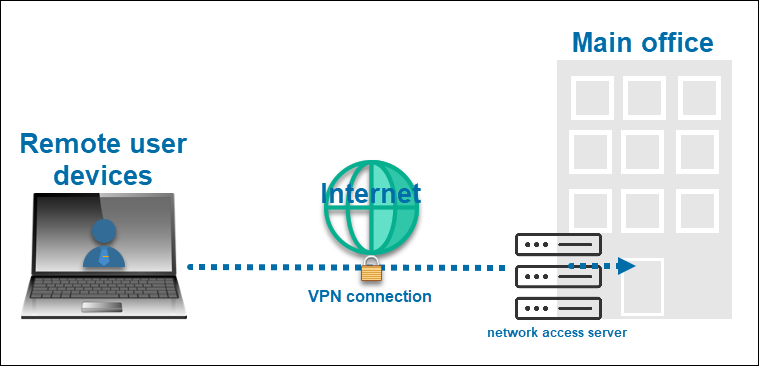
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, and it serves to create a secure tunnel between an endpoint device and another network. It is commonly used to allow secure remote access for employees from various devices such as PCs or laptops.
Since users are accessing a private network that contains possible confidential data, it is crucial to ensure the safe transmission of data from one network to another. As there are many potential threats of doing so over the internet, creating a so-called tunnel ensures corporate resources do not fall into the wrong hands. A VPN establishes a connection by encrypting all traffic between the two networks and masking the IP addresses.
Note: Protecting endpoint devices helps in preventing ransomware.
Administrators configure the VPN access policy and set up the shared resources. Therefore, users only have remote access to the resources within the defined system. They can download and store the data on their personal computers and work on them offline.
What is VDI?
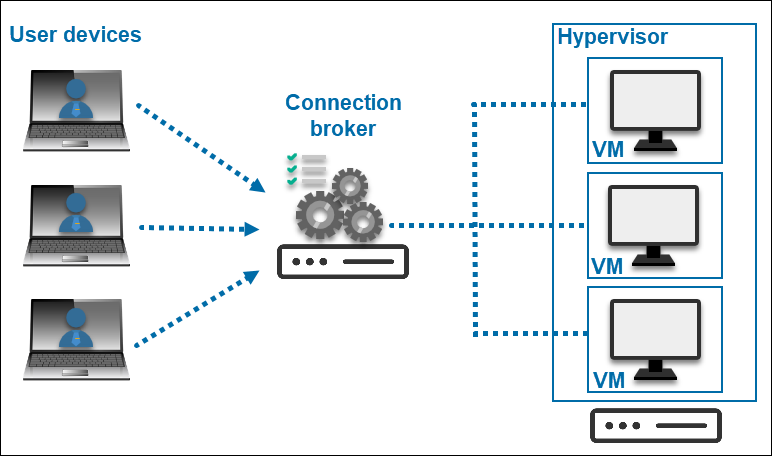
VDI is short for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, and it represents a system in which hosted desktop environments are virtualized and transmitted to users over a network. A single dedicated server hosted in a data center (or office) runs multiple virtual machines. Each VM runs a desktop environment and provides remotely accessible workstations.
This virtual network computing system provides dedicated workstations and resources, ensuring high performance. Users can connect to their virtual desktop from any remote device. VDI is device-agnostic and it doesn’t rely on the end-user hardware.
VDI has a centralized management system in which administrators take care of OS updates and configuration. It is simple to install new software and maintain workstations by utilizing the golden image. This golden image gets replicated across multiple desktops inside a cluster.
Note: For more information about virtual desktop infrastructure, check out our article What is VDI and How Does it Work.
VPN vs. VDI: What are the Differences?
Although they seem similar at first glance, VDI and VPN work differently and provide different services. While VDI allows access to a remote desktop on which users can work, VPN establishes a tunnel between the end-user and an organization’s private network.
However, as they are both popular solutions for remote work, many employers are unsure which to choose for their business. Therefore, it is best to compare each solution head-to-head to see which one fits best for your specific use case.
| VPN | VDI | |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Highly dependent on end-user resources | Minimal hardware requirements from the end user |
| Data Storage and Security | Data encryption and the ability to copy files to local device | Can restrict users from moving or copying data to local devices |
| Performance | Limited by end-user resources and connection speed | Has allocated server resources for each user |
| Management and Maintenance | More difficult to manage and troubleshoot when working with off-site resources | A centralized management system configures and maintains all workstations |
| Cost | Cost-effective due to minimal resource requirements | More expensive as it required additional software and hardware |
Hardware
VPN is highly dependent on user hardware since all the processing is done on client devices. Older hardware and outdated operating systems can impact performance and affect productivity.
On the other hand, VDI has minimal hardware requirements, and end-user devices are unimportant for the overall experience. Processing is done server-side using dedicated resources assigned to the virtual machine running the virtual desktop. It is common to use cheap or outdated devices, thin clients, for VDI.
Data Storage and Security
There is a big difference in how VPN and VDI handle data. VPN protects the data while it is in transit, sending it over an encrypted tunnel. While the tunneled data arrives safely to the user, it has no security limits once it is on the client’s machine. It can be moved and copied to the client’s devices without restrictions. Having company files copied locally can present a danger for a potential data breach.
When using VDI, applications, and data remain on the virtual machine running the workstation. Therefore, files are protected on company servers or the cloud. Administrators can configure virtual desktops to restrict moving data outside the corporate network.
Performance
Without a doubt, VPN loses the race performance-wise for larger workloads. Since virtual private networks rely on the end-user devices, it is limited to the end-user resources and connection speed. Therefore, different users have different performance results depending on their hardware and connection quality. Additionally, encrypting and decrypting large amounts of data can also impact the overall speed.
VDI provides a faster environment and better UX because each user has allocated resources for their workstation. Instead of having to rely on the user’s devices, VDI uses dedicated server resources to improve customization and performance capabilities.
Management and Maintenance
When it comes to VPN management, the VPN server itself is easier and less expensive to maintain. However, maintaining the client devices is more complex since they are utilizing off-site resources. This requires connecting to the device for troubleshooting or updates.
Unlike with VPN, admins can easily update and fix issues on a virtual desktop infrastructure because they have a centralized system management. With centralized access, admins can update multiple devices at once and have close control over the system. Still, maintaining such a system also includes running and managing multiple VMs for different functioning. Due to the system's complexity, this solution requires skilled admins who can configure and ensure everything is set up properly.
Cost
Cost may play a big role when deciding between VPN and VDI as it differs drastically. If you are searching for a cost-effective solution, VPN is the way to go. Due to its minimal hardware requirements and less expensive maintenance, VPN is the lowest-cost system. It utilizes users' devices and can cover multiple devices through a single account.
Contrary to VPN, VDI is a more expensive solution for remote work. It includes adding an extra layer of software for hosting the VDI system, server hardware, and dedicated resources for each workstation, which costs a lot of money.
VPN vs VDI: Which One is Better?
There is no simple answer to the question of whether VPN or VDI is better. Generally, it depends on your specific use case and the factors that play a significant role.
To sum up, VPN is more suitable for smaller businesses as it is cost-effective, easy to implement, and simple to use. However, if you are dealing with a larger workforce where high performance and graphic processing is required, VDI is a better choice.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you should have a better understanding about the difference between VPN and VDI. You should know how both solutions work and which one would fit better for your business needs.