Linux packages are compressed archives containing programs and files necessary to run them. The package distribution system is designed to be robust and simplify the application installation process.
However, a bad internet connection or misconfigured third-party installers sometimes corrupt packages and cause problems on your system.
This article will show you how to troubleshoot and fix broken packages on Ubuntu using the available APT and DPKG tools.

Prerequisites
Check for Updates
Start troubleshooting by rebuilding the list of dependencies. The --fix-missing option updates the list of available packages while ignoring any missing dependencies.
This option ensures the update process is performed without APT returning an error. It also allows users to address missing packages later without interrupting the update process.
Run the following command:
sudo apt update --fix-missing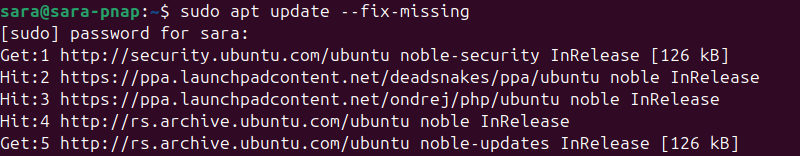
Force APT to Correct Missing Dependencies or Broken Packages
Missing package dependencies are a common reason for package-related errors. To fix this problem, use apt install with the -f flag.
The command tells APT to locate the missing packages and install them:
sudo apt install -f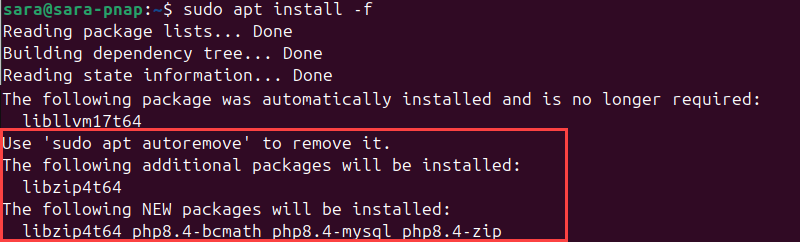
Note: If troubleshooting has led to Ubuntu needing to be reinstalled, please refer to our reinstallation guide on how to reinstall Ubuntu.
Force Reconfigure or Remove Broken Packages with DPKG
Broken packages sometimes cause package manager configuration problems. To fix this issue, take the following steps:
1. Reconfigure DPKG, the base package management system, with the following command:
sudo dpkg --configure -aThe command configures packages that have not yet been configured on the system. If there's no output, it means all packages are already properly configured, or there were no packages that needed configuring.
However, if a package cannot be configured, the command produces an output:
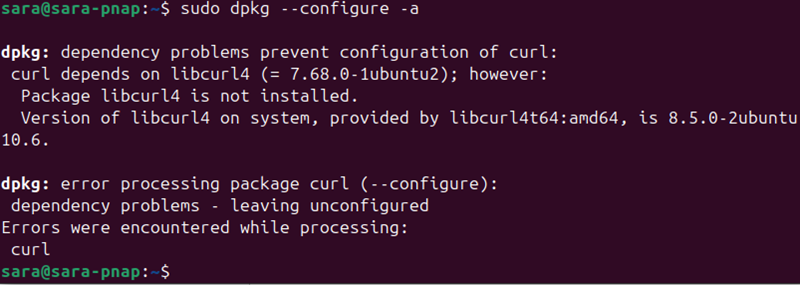
The output shows the curl package has a dependency problem, which prevents it from being configured properly. Fix it by installing the missing dependencies with:
sudo apt install [missing-package]2. Check for leftover configuration files. Run the following command:
sudo dpkg -l | grep ^..RThe command checks for removed packages, but the configuration files remain on the system. If there is no output, there are no packages in this state.
If there is an output, it indicates one or more packages were removed, but their configuration files remain.
On Ubuntu 24.04, however, the system is often aggressive in cleaning up configuration files during package removal, so it's common to see no output.
3. Remove leftover configuration files with:
sudo dpkg --purge --force-all [package-name]For example, to remove the corrupted vlc-plugin-base package, run:
sudo dpkg --purge --force-all vlc-plugin-base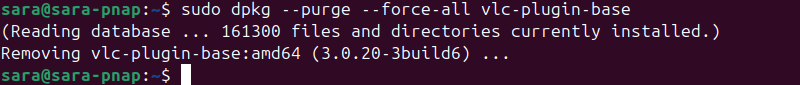
Warning: The dpkg --purge --force-all command removes a package even if the removal causes further dependency issues. Use the command with care.
4. Run the following command to clean up the system:
sudo apt cleanThe command has no output.
5. Update the repositories again:
sudo apt updateResolve DPKG Lock Issue
The DPKG lock error appears when you try to install a package while another process is using DPKG. For example:
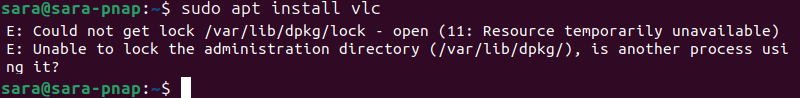
However, sometimes, the error occurs even if no other processes are using the package management system.
To fix the problem, remove the lock file manually:
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lockThe command has no output.
Also, remove the lock in cache:
sudo rm /var/cache/apt/archives/lockThe command also doesn't produce any output. However, deleting the lock enables you to use APT and DPKG again.
Note: Ubuntu 24.04 often doesn't display the DPKG lock error because it automatically manages and resolves lock file conflicts in the background. This means the issue is handled without interrupting the user with an explicit error message.
Conclusion
The article explained how to fix broken packages on Ubuntu using several different methods. It also elaborated on how to solve the DPKG lock issue.
Next, learn how to list installed packages on Ubuntu.